dBm
dBm (sometimes dBmW) is an abbreviation for the power ratio in decibels (dB) of the measured power referenced to one milliwatt (mW). It is used in radio, microwave and fiber optic networks as a convenient measure of absolute power because of its capability to express both very large and very small values in a short form. Compare dBW, which is referenced to one watt (1000 mW).
Since it is referenced to the watt, it is an absolute unit, used when measuring absolute power. By comparison, the decibel (dB) is a dimensionless unit, used for quantifying the ratio between two values, such as signal-to-noise ratio.
Zero dBm equals one milliwatt. A 3 dB increase represents roughly doubling the power, which means that 3 dBm equals roughly 2 mW. For a 3 dB decrease, the power is reduced by about one half, making −3 dBm equal to about 0.5 milliwatt. To express an arbitrary power P as x dBm, or go in the other direction, the following equations may be used:
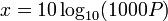 or,
or, 
and
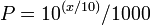 or,
or, 
where P is the power in W and x is the power ratio in dBm. Below is a table summarizing useful cases:
| 60 dBm | 1 kW = 1000 W | Typical combined radiated RF power of microwave oven elements |
| 80 dBm | 100 kW | Typical transmission power of FM radio station with 50 km range |
 I designed this blog to help and get benefited by their deeds in my career.I hope you all utilise this opportunity and get benefited.
****Feel free to contact me *****
I will soon update remaining........
keep visiting ........
I designed this blog to help and get benefited by their deeds in my career.I hope you all utilise this opportunity and get benefited.
****Feel free to contact me *****
I will soon update remaining........
keep visiting ........

No comments:
Post a Comment